Load Balancing
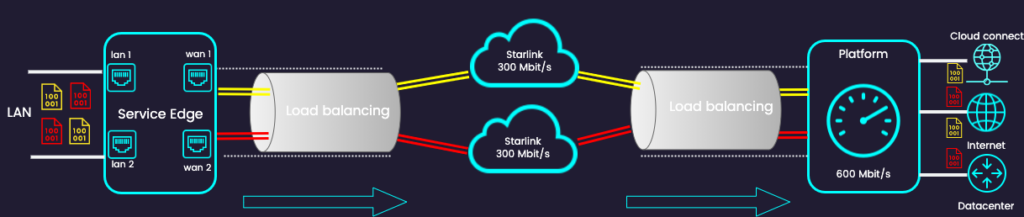
Load Balancing is a technique that dynamically distributes network traffic across multiple Wide Area Network (WAN) connections.
These can be various internet connections, such as fiber, DSL, 5G, or satellite (like Starlink). The goal is to make optimal use of the available bandwidth, handle connection failures, and improve overall network performance.
Continuous analysis
The balancing principle ensures that traffic flows are continuously analyzed and directed over the most suitable path based on actual load conditions.
In case of a failure in one of the connections, our Service Edge will automatically reroute traffic via another WAN connection to our platform.
Improved performance
Load balancing intelligently distributes the workload across two or more WAN connections without relying on complex routing protocols like BGP. This approach optimizes system performance.
In many cases, a pleasant side effect of having two or more internet connections is the lower overall operational costs of the internet service.
This is achieved because similar capacity with a single ISP is generally more costly or may not even be available, especially in the case of high-capacity lines.
Automatic failover
In addition, WAN load balancing provides failover: if one connection goes down, traffic is automatically redirected through another available connection, without users noticing.
Benefits
- Maximizing the use of all available bandwidth
- Highest possible performance
- Increased reliability
- Always connected, even during outages
Frequently Asked Questions about Load Balancing
In most cases, it refers to the technique that distributes network traffic across two separate internet connections to improve network availability.
Want to know more?
Leave a message using the form below, and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
Wanscale
Wanscale B.V.
Trivium 76
4873 LP Etten-Leur
088-1223400
info@wanscale.com